===============================
Download
Where can I get DataTorrent RTS software?
DataTorrent products are available for download from https://www.datatorrent.com/download/
- Community Edition: It is a packaged version of Apache Apex and enables developers to quickly develop their big data streaming and batch projects.
- Enterprise Edition: Designed for enterprise production deployment and includes security, advanced monitoring and troubleshooting, graphical application assembly, and application data visualization.
- Sandbox Edition: Enterprise Edition and demo applications pre-installed and configured with a single-node Hadoop cluster running in a virtual machine. Optimized for evaluation and training purposes.
What is the difference between DataTorrent RTS editions?
Please refer to DataTorrent RTS editions overview
What are DataTorrent RTS package contents of Community vs Enterprise edition?
Package contents for Community edition:
- Apache Apex
- DataTorrent Demo Applications
- DataTorrent dtManage
Package contents for Enterprise edition:
- Apache Apex
- DataTorrent Demo Applications
- DataTorrent Operator Library
- DataTorrent Enterprise Security
- DataTorrent dtManage
- DataTorrent dtAssemble
- DataTorrent dtDashboard
How do I confirm the package downloaded correctly?
You can verify the downloaded DataTorrent RTS package by comparing with MD5 sum. The command to get md5 sum of downloaded package:
# md5sum <DT_RTS_Package>
Compare the result with MD5 sum posted on the product download page.
How do I download the DataTorrent RTS package using CLI?
Use following curl command to download DataTorrent RTS package:
curl -LSO <DT_RTS_download_link>
We recommend using ‘curl’ instead of ‘wget’, which lacks chunked transfer encoding support, potentially resulting in corrupted downloads.
What are the prerequisites of DataTorrent RTS ?
DataTorrent RTS platform has following Hadoop cluster requirements:
- Operating system supported by Hadoop distribution
- Hadoop (2.2 or above) cluster with HDFS, YARN configured. Make sure hadoop executable available in PATH variable
- Java 7 or 8 as supported by Hadoop distribution
- Minimum of 8G RAM available on the Hadoop cluster
- Permissions to create HDFS directory for DataTorrent user
- Google Chrome or Safari to access dtManage (DataTorrent UI console)
Where can I start from after downloading DataTorrent RTS?
- After successful download of DataTorrent RTS, make sure all prerequisites are satisfied.
- You will need to install DataTorrent RTS on Hadoop cluster using the downloaded installer. Refer to installation guide
- Once installed, you will be prompted to proceed to dtManage, the DataTorrent management console, where you will be able to launch and manage applications.
What are the supported Hadoop distribution by DataTorrent RTS?
DataTorrent RTS is a Hadoop 2.x native application and is fully integrated with YARN and HDFS providing tight integration with any Apache Hadoop 2.x based distribution.
Hadoop Distribution |
Supported Version |
Amazon EMR |
Hadoop 2.4 and higher |
Apache Hadoop |
Hadoop 2.2 and higher |
Cloudera |
CDH 5.0 and higher |
Hortonworks |
HDP 2.0 and higher |
MapR |
4.0 and higher |
Microsoft |
HDInsight |
Pivotal |
2.1 and higher |
What is the Datatorrent Sandbox?
The Sandbox provides a quick and simple way to experience DataTorrent RTS without setting up and managing a complete Hadoop cluster. The Sandbox contains pre-installed DataTorrent RTS Enterprise Edition along with all the Hadoop services required to launch and run the included demo applications.
Where do I get DataTorrent Sandbox download link?
Sandbox can be downloaded by visiting datatorrent.com/download
What are the system requirements for sandbox deployment?
The DataTorrent RTS Sandbox is a complete, stand-alone, instance of the Enterprise Edition as a single-node Hadoop cluster on your local machine. Following are prerequisites for DataTorrent RTS:
- VirtualBox 4.3 or greater installed.
- 6GB RAM or greater available for Sandbox VM.
What are the DataTorrent RTS package content details in sandbox?
- Ubuntu 12.04 LTS + Apache Hadoop 2.2 (DataTorrent RTS 3.1 or earlier)
- Lubuntu 14.04 LTS + Apache Hadoop 2.7 (DataTorrent RTS 3.2 or later)
- Apache Apex, Apache Apex-Malhar
- DataTorrent Operator Library
- DataTorrent Enterprise Security
- DataTorrent dtManage
- DataTorrent dtAssemble
- DataTorrent dtDashboard
- Demo Applications
Why does the browser console on the sandbox say HDFS Not Ready ?
The HDFS services take a few minutes to start; the console needs all of
those services to be up and running and until that occurs, it displays this
warning. If the normal console does not appear after a few minutes, please run
the jps command to see which services may not be running, for example:
dtadmin@dtbox:~/tmp$ jps
1407 DTGateway
4145 Jps
2830 NodeManager
3059 ResourceManager
2650 NameNode
Here we see that the DataNode is not running. In this case, stop all
HDFS services (using, for example the script shown in the
sandbox page. Then, remove everything
under these directories:
/sfw/hadoop/shared/data/hdfs/datanode/current
/sfw/hadoop/shared/data/hdfs/namenode/current
Now reformat HDFS with hdfs namenode -format
and finally, restart all HDFS services.
If all services are running and the normal console still does not appear, please run following commands:
hdfs dfsadmin -safemode leave
hdfs fsck -delete
If HDFS detects that some files are corrupted (perhaps due to an earlier improper shutdown) it will not exit the initial safemode automatically; the commands above exit safemode manually and delete corrupted files.
How do I get specific DT version ?
You can find archive list of various DataTorrent RTS versions at the bottom of each product download page.
Where can I request new / upgrade current license?
Please follow the instructions at License Upgrade
Where do I find product documentation?
Please refer to: DataTorrent Documentation
Where can I learn more about Apache Apex?
You can refer Apex page for more details: Apache Apex
Do you need help?
You can contact us at https://www.datatorrent.com/contact
Installation
There are multiple installations available e.g. Sandbox Edition, Community Edition, Enterprise Edition, dtIngest. Supported operating systems are which support Hadoop platform (tested on CentOS 6.x and Ubuntu 12.04).
Minimum hardware requirements, what happens if certain minimum configuration requirement has not been met?
Minimum of 8G RAM is required on the Hadoop cluster.
What happens if java is not installed?
Following message can be seen when Java is not available on the system
Error: java executable not found. Please ensure java
or hadoop are installed and available in PATH environment variable
before proceeding with this installation.
Install Java 7 from package manager of Linux Distribution and try running installer again.
What happens if Hadoop is not installed?
Installation will be successful, however Hadoop Configuration page in dtManage (e.g. http://localhost:9090) will expect Hadoop binary (/usr/bin/hadoop) & DFS location.
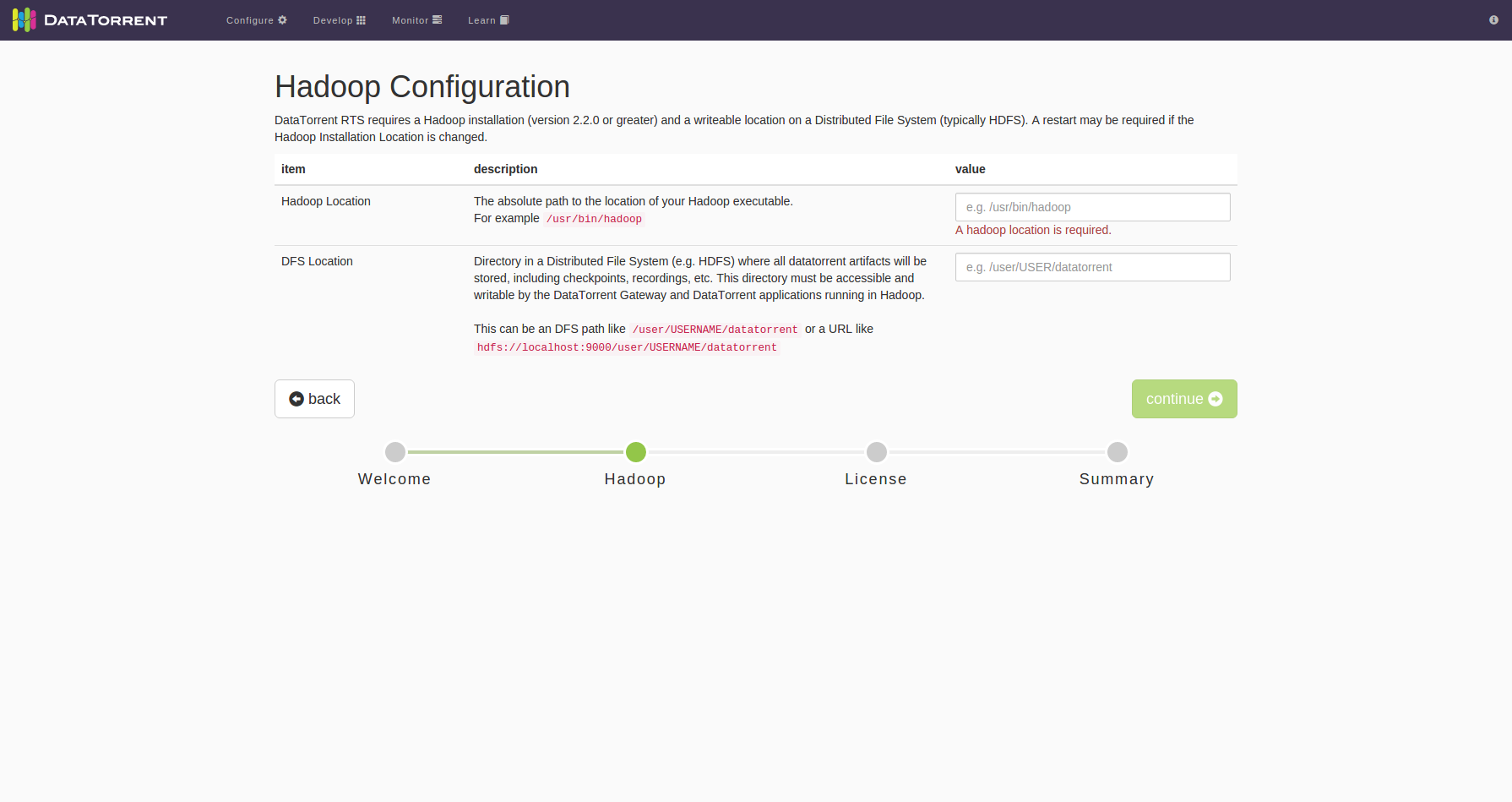
Install Hadoop > 2.2.0 and update the configuration parameters above.
How do I check if Hadoop is installed and running correctly?
Following commands can be used to confirm installed Hadoop version and if Hadoop services are running.
$ hadoop version
Hadoop 2.4.0
Subversion [http://svn.apache.org/repos/asf/hadoop/common](http://svn.apache.org/repos/asf/hadoop/common) -r
1583262
Compiled by jenkins on 2014-03-31T08:29Z
Compiled with protoc 2.5.0
From source with checksum 375b2832a6641759c6eaf6e3e998147
This command was run using
/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/common/hadoop-common-2.4.0.jar
$ jps
10211 NameNode
10772 ResourceManager
10427 DataNode
14691 Jps
10995 NodeManager
What happens if the downloaded file is corrupted?
MD5 checksum will result in the following error:
“Verifying archive integrity...Error in MD5 checksums: <MD5 checksum> is different from <MD5 checksum>”.
Downloaded installer could be corrupted. Try downloading the installer again. If using command line, use curl instead of wget.
Why do I see the following permissions errors?
During installation following error message will be seen on screen
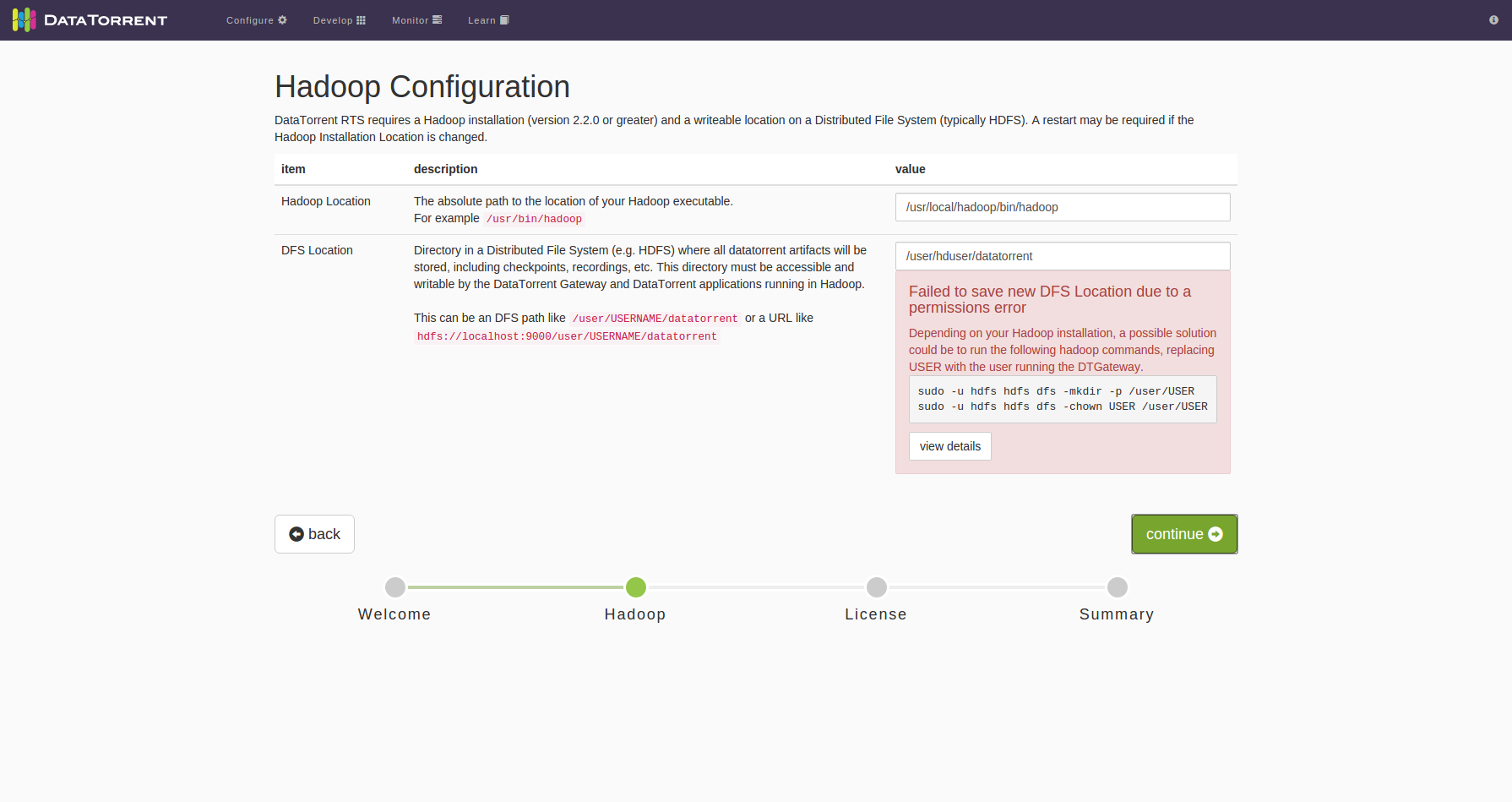
These typically happen when specified directory does not exist, and the installation user does not have permissions to create it. Following commands can be executed by user with sufficient privileges to resolve this issue:
$ hadoop dfs -ls /user/<USER>/datatorrent
$ hadoop dfs -mkdir /user/<USER>/datatorrent
$ hadoop dfs -chown <USER> /user/<USER>/datatorrent
Upgrade
License agent errors cause problems during upgrade from DataTorrent RTS 2.0 to 3.0.
If your applications are being launched continuously, or you are unable to launch apps due to licensing errors, try running complete uninstall and re-installation of DataTorrent RTS. See installation guide for details.
Configuration
Configuring Memory
Configuring Operator Memory:
Operator memory for an operator can be configured in one of the following two ways:
1 Using the same default values for all the operators:
<property>
<name>dt.application.<APPLICATION_NAME>.operator.*.attr.MEMORY_MB</name>
<value>2048</value>
</property>
This would set 2GB as size of all the operators in the given application.
2 Setting specific value for a particular operator: Following example will set 8GB as the operator memory for operator Op.
<property>
<name>dt.application.<APPLICATION_NAME>.operator.Op.attr.MEMORY_MB</name>
<value>8192</value>
</property>
The amount of memory required by an operator should be based on maximum amount of data that operator will be storing in-memory for all the fields -- both transient and non-transient. Default value for this attribute is 1024 MB.
Configuring Buffer Server Memory:
There is a buffer server in each container hosting an operator with an output port connected to an input port outside the container. The buffer server memory of a container can be controlled by BUFFER_MEMORY_MB. This can be configured in one of the following ways:
1 Using the same default values for all the output ports of all the operators
<property>
<name>dt.application.<APPLICATION_NAME>.operator.*.port.*.attr.BUFFER_MEMORY_MB</name>
<value>128</value>
</property>
This sets 128Mb as buffer memory for all the output ports of all the operators.
2 Setting specific value for a particular output port of particular operator: Following example sets 1GB as buffer memory for output port p of an operator Op:
<property>
<name>dt.application.<APPLICATION_NAME>.operator.Op.port.p.attr.BUFFER_MEMORY_MB</name>
<value>1024</value>
</property>
Default value for this attribute is 512 MB
Calculating Container memory:
Following formula is used to calculate the container memory.
Container Memory = Sum of MEMORY_MB of All the operators in the container+ Sum of BUFFER_MEMORY_MB of all the output ports that have a sink in a different container.
Sometimes the memory allocated to the container is not same as calculated by the above formula, it is because actual container memory allocated by RM has to lie between
[yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb, yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb]
These values can be found in yarn configuration
Configuring Application Master Memory:
Application Master memory can be configured using MASTER_MEMORY_MB attribute. Following example sets 4GB as the memory for Application Master:
<property>
<name>dt.application.<APPLICATION_NAME>.attr.MASTER_MEMORY_MB</name>
<value>4096</value>
</property>
Default value for this attribute is 1024 MB. You may need to increase this value if you are running a big application that has large number of containers
Development
Hadoop dependencies conflicts
You have to make sure that the Hadoop jars are not bundled with the application package o/w they may conflict with the versions available in Hadoop classpath. Here are some of the ways to exclude Hadoop dependencies from the application package
-
If your application is directly dependent on the Hadoop jars, make sure that the scope of the dependency is
provided. For eg if your application is dependent on hadoop-common, this is how you should add the dependency in pom.xml<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId> <artifactId>hadoop-common</artifactId> <version>2.2.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> -
If your application has transitive dependency on Hadoop jars, make sure that Hadoop jars are excluded from the transitive dependency and added back as application dependency with provided scope as mentioned above. Exclusions in pom.xml can be set as follows
<dependency> <groupId></groupId> <artifactId></artifactId> <version></version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId> <artifactId>*</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>
Serialization considerations
The platform requires all operators and tuples in an Apex application to be serializable (and deserializable). After an application is launched, operators are serialized from the starting node and deserialized and instantiated on various cluster nodes. Also checkpointing involves serializing and persisting an operator to a store and deserializing from the store in case of recovery. Tuples are serialized and deserialized when transmitted over a stream.
Problems of lack of serializability (and deserializability) in the code can only be reliably uncovered at run-time.
So the recommended way to uncover these problems is to run the application in
local mode before running on a cluster.
Use the ApexCLI to launch your application with the -local option
to run it in local mode. When the platform runs into a situation where a field or object is not serializable or
deserializable, the application will fail at that point with a relevant exception logged on the console or the
log file as described in the Kryo exception section. Check out
that section further for hints about troubleshooting serialization issues.
Transient members
Certain data members of an operator do not need to be serialized or deserialized during deployment or checkpointing/recovery because they are transient in nature and do not represent stateful data. Developers should judiciously use the transient keyword for declaring such non-stateful members of operators (or members of objects which are indirectly members of operators) so that the platform skips serialization of such members and serialization/deserialization errors are minimized. Transient members are further described in the context of the operator life-cycle here. Typical examples of transient data members are database or network connection objects which need to be initialized before they are used in a process, so there is no use of persisting them across process invocations.
Getting this message in STRAM logs. Is anything wrong in my code?
2015-10-09 04:31:06,749 INFO com.datatorrent.stram.StreamingContainerManager: Heartbeat for unknown operator 3 (container container_1443694550865_0150_01_000007)
Coming soon.
Debugging
How to remote debug gateway service?
Update Hadoop OPTS variable by running,
export HADOOP_OPTS="-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=y,address=5432 $HADOOP_OPTS"
How to setup DEBUG level while running an application?
Add the following property to your properties file:
<property>
<name>dt.application.<APP-NAME>.attr.DEBUG</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
My gateway is throwing the following exception.
ERROR YARN Resource Manager has problem: java.net.ConnectException: Call From myexample.com/192.168.3.21 to 0.0.0.0:8032 failed on connection
exception: java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused; For more details see:[http://wiki.apache.org/hadoop/ConnectionRefused](http://wiki.apache.org/hadoop/ConnectionRefused) at
sun.reflect.GeneratedConstructorAccessor27.newInstance(Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.java:45)
...
Check if the host where gateway is running has yarn-site.xml file. You need to have all Hadoop configuration files accessible to dtGateway for it to run successfully.
When Apex is running in secure mode, YARN logs get flooded with several thousand messages per second.
Please make sure that the kerberos principal user name has an account with the same user id on the cluster nodes.
Application throwing following Kryo exception.
com.esotericsoftware.kryo.KryoException: Class cannot be created (missing no-arg constructor):
This means that Kryo is not able to deserialize the object because the type is missing default constructor. There are couple of ways to address this exception
- Add default constructor to the type in question.
-
Using custom serializer for the type in question. Some existing alternative serializers can be found at https://github.com/magro/kryo-serializers. A custom serializer can be used as follows:
2.1 Using Kryo's @FieldSerializer.Bind annotation for the field causing the exception. Here is how to bind custom serializer.
@FieldSerializer.Bind(CustomSerializer.class) SomeType someTypeKryo will use this CustomSerializer to serialize and deserialize type SomeType. If SomeType is a Map or Collection, there are some special annotations @BindMap and @BindCollection; please see here.
2.2 Using the @DefaultSerializer annotation on the class, for example:
@DefaultSerializer(JavaSerializer.class) public class SomeClass ...2.3 Using custom serializer with stream codec. You need to define custom stream codec and attach this custome codec to the input port that is expecting the type in question. Following is an example of creating custom stream codec:
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.util.UUID; import com.esotericsoftware.kryo.Kryo; public class CustomSerializableStreamCodec<T> extends com.datatorrent.lib.codec.KryoSerializableStreamCodec<T> { private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { in.defaultReadObject(); this.kryo = new Kryo(); this.kryo.setClassLoader(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()); this.kryo.register(SomeType.class, new CustomSerializer()); // Register the types along with custom serializers } private static final long serialVersionUID = 201411031405L; }Let's say there is an Operator
CustomOperatorwith an input portinputthat expects type SomeType. Following is how to use above defined custom stream codecCustomOperator op = dag.addOperator("CustomOperator", new CustomOperator()); CustomSerializableStreamCodec<SomeType> codec = new CustomSerializableStreamCodec<SomeType>(); dag.setInputPortAttribute(op.input, Context.PortContext.STREAM_CODEC, codec);This works only when the type is passed between different operators. If the type is part of the operator state, please use one of the above two ways.
Log analysis
There are multiple ways to adjust logging levels. For details see configuration guide.
How to check STRAM logs
You can get STRAM logs by retrieving YARN logs from command line, or by using dtManage web interface.
In dtManage console, select first container from the Containers List in Physical application view. The first container is numbered 000001. Then click the logs dropdown and select the log you want to look at.
Alternatively, the following command can retrieve all application logs, where the first container includes the STRAM log.
yarn logs -applicationId <applicationId>
How to check application logs
On dt console, select a container from the Containers List widget (default location of this widget is in the “physical” dashboard). Then click the logs dropdown and select the log you want to look at.
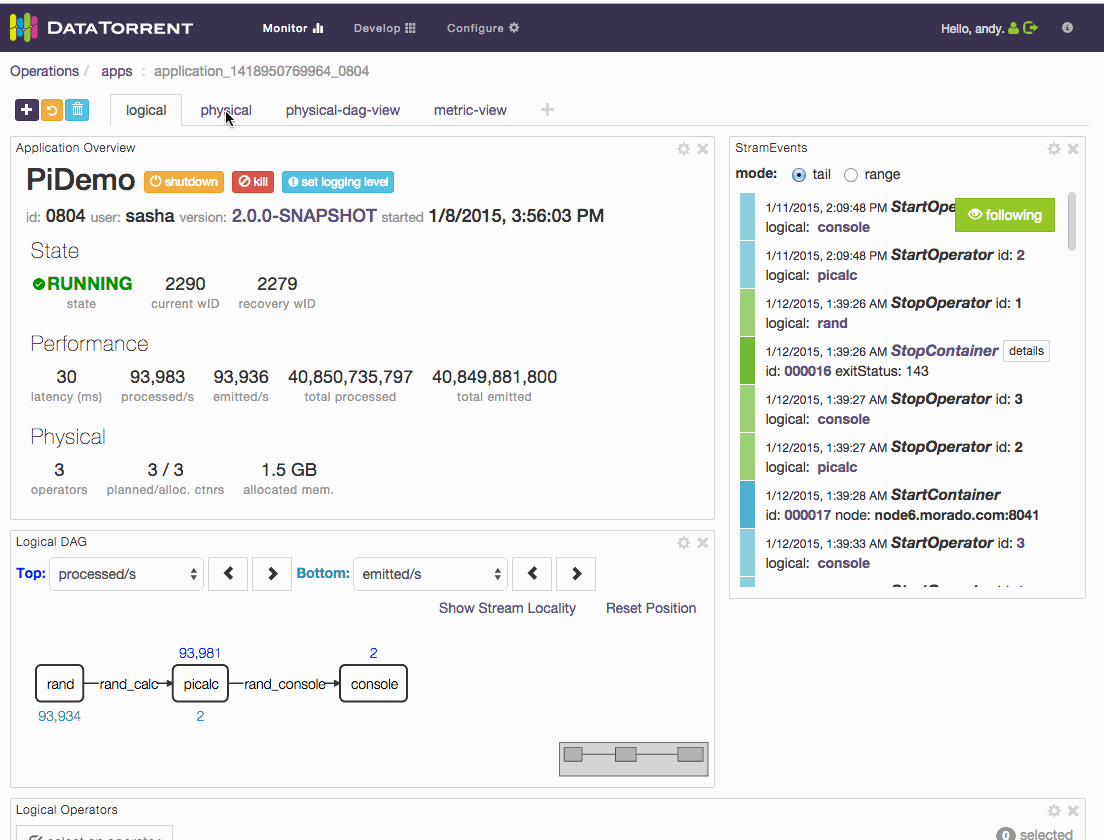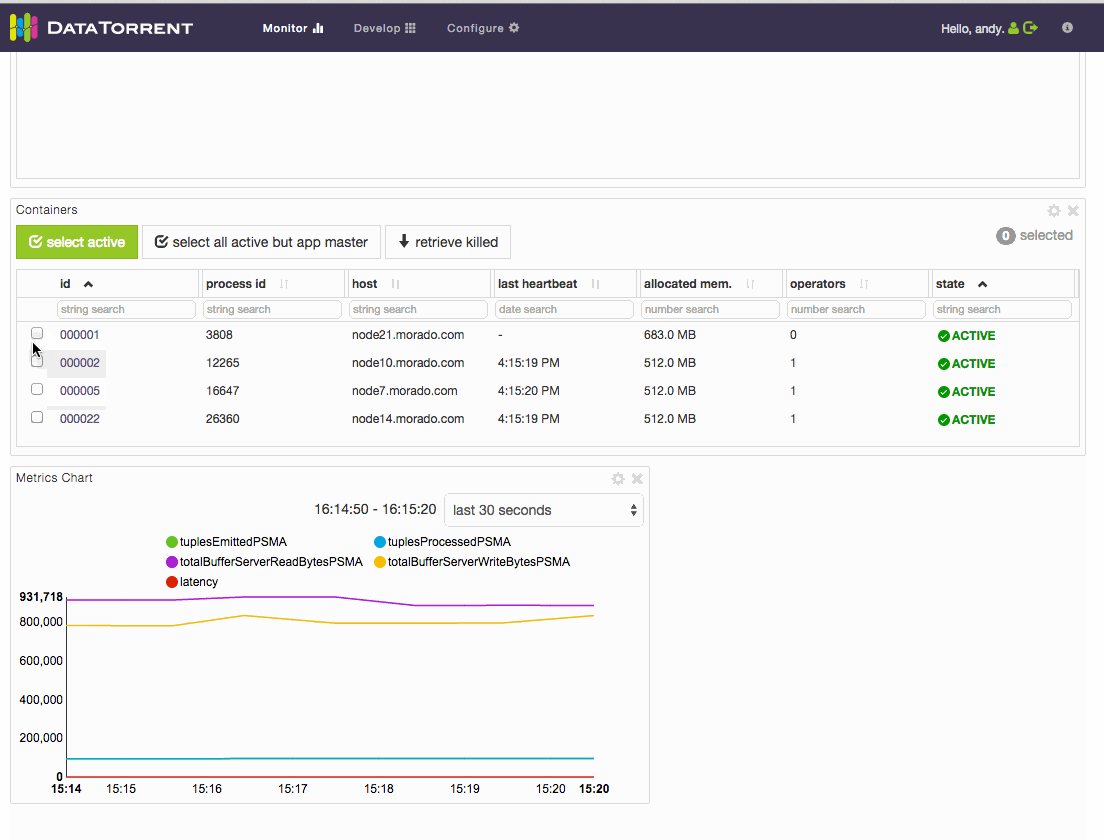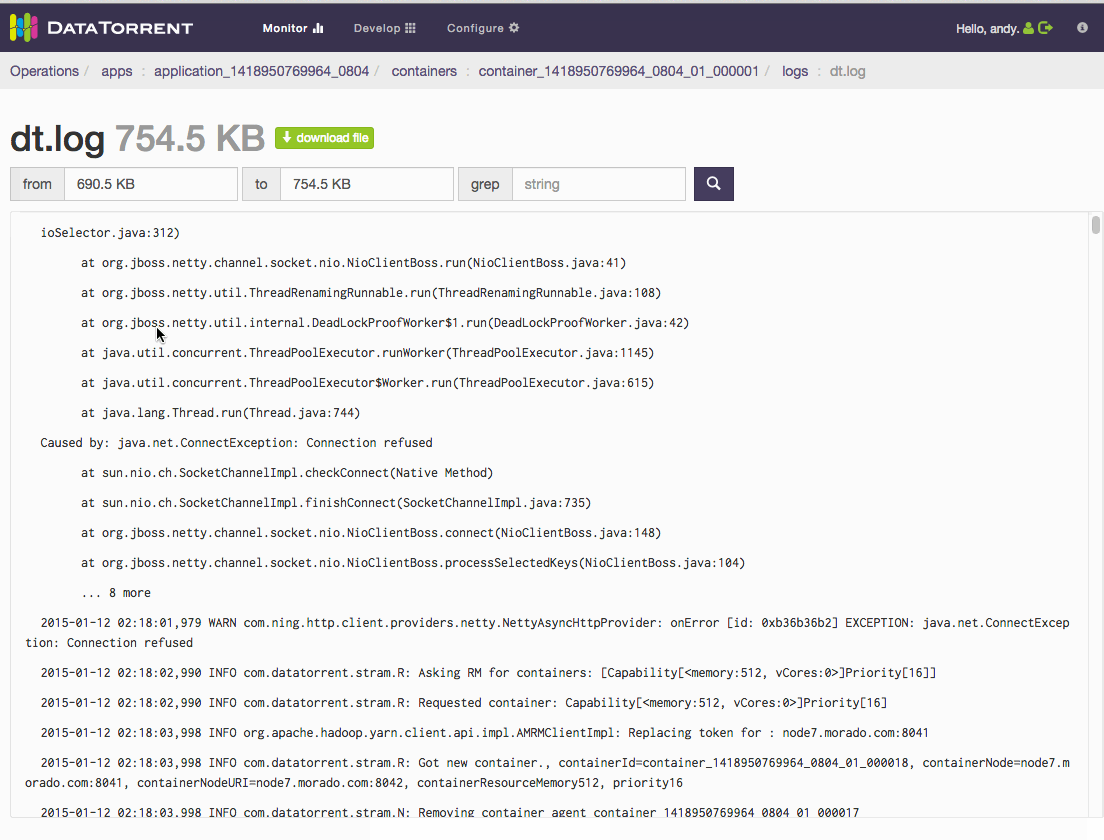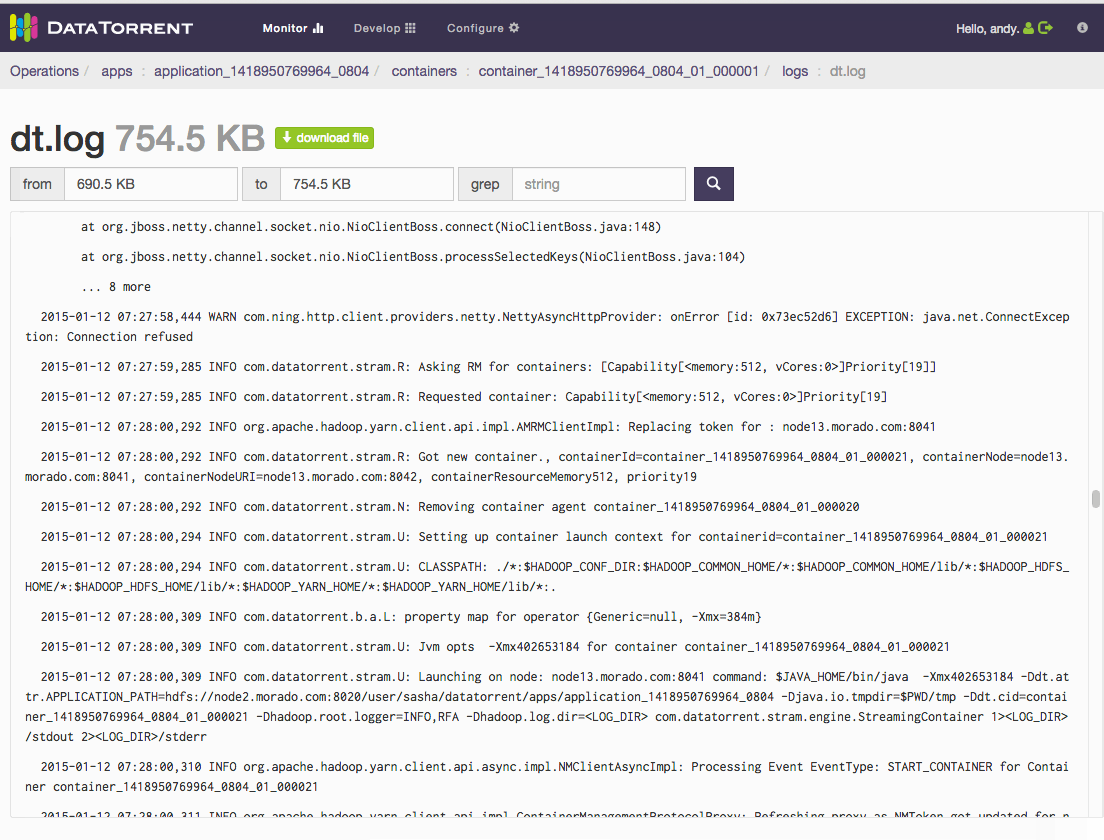
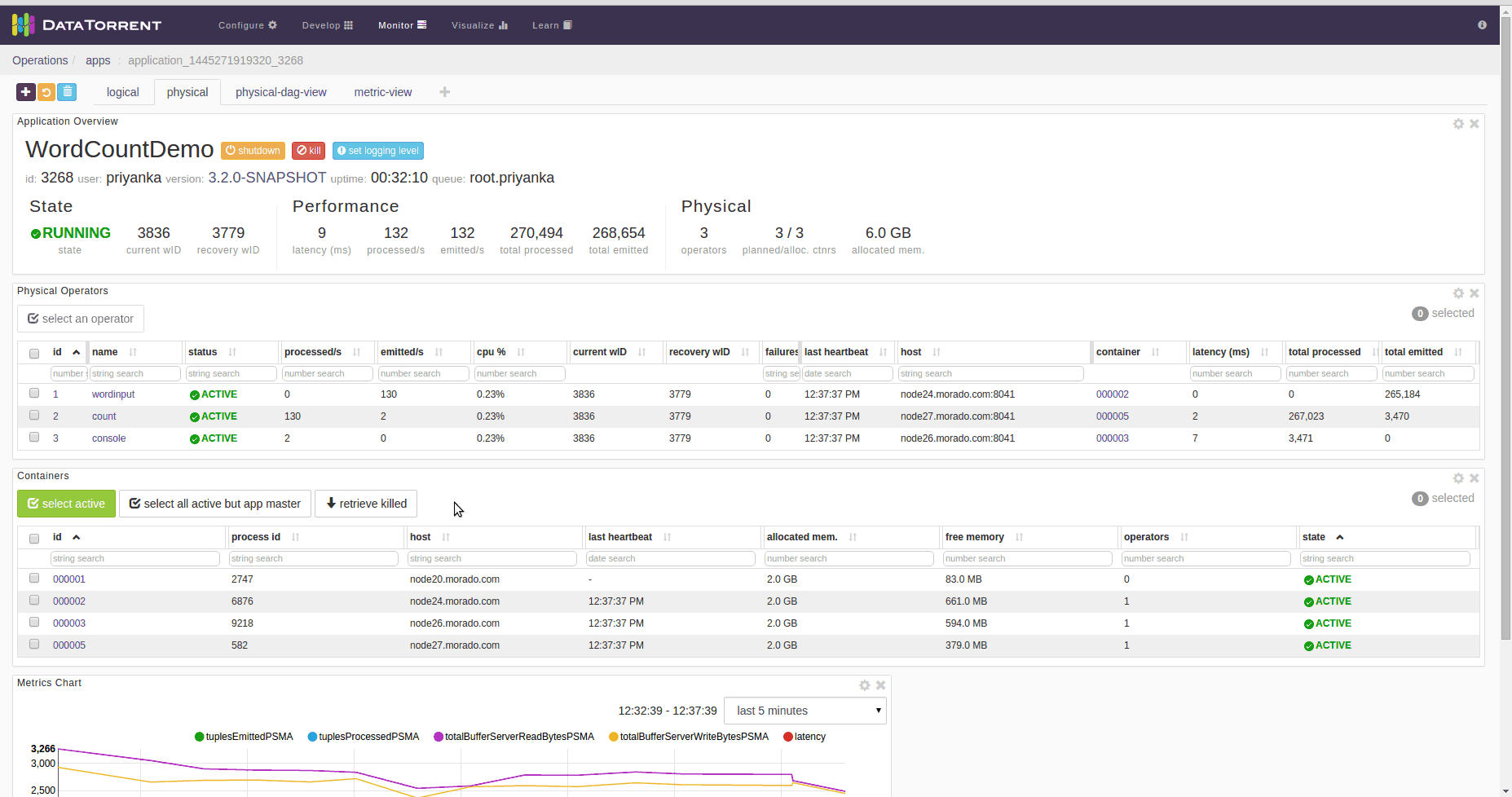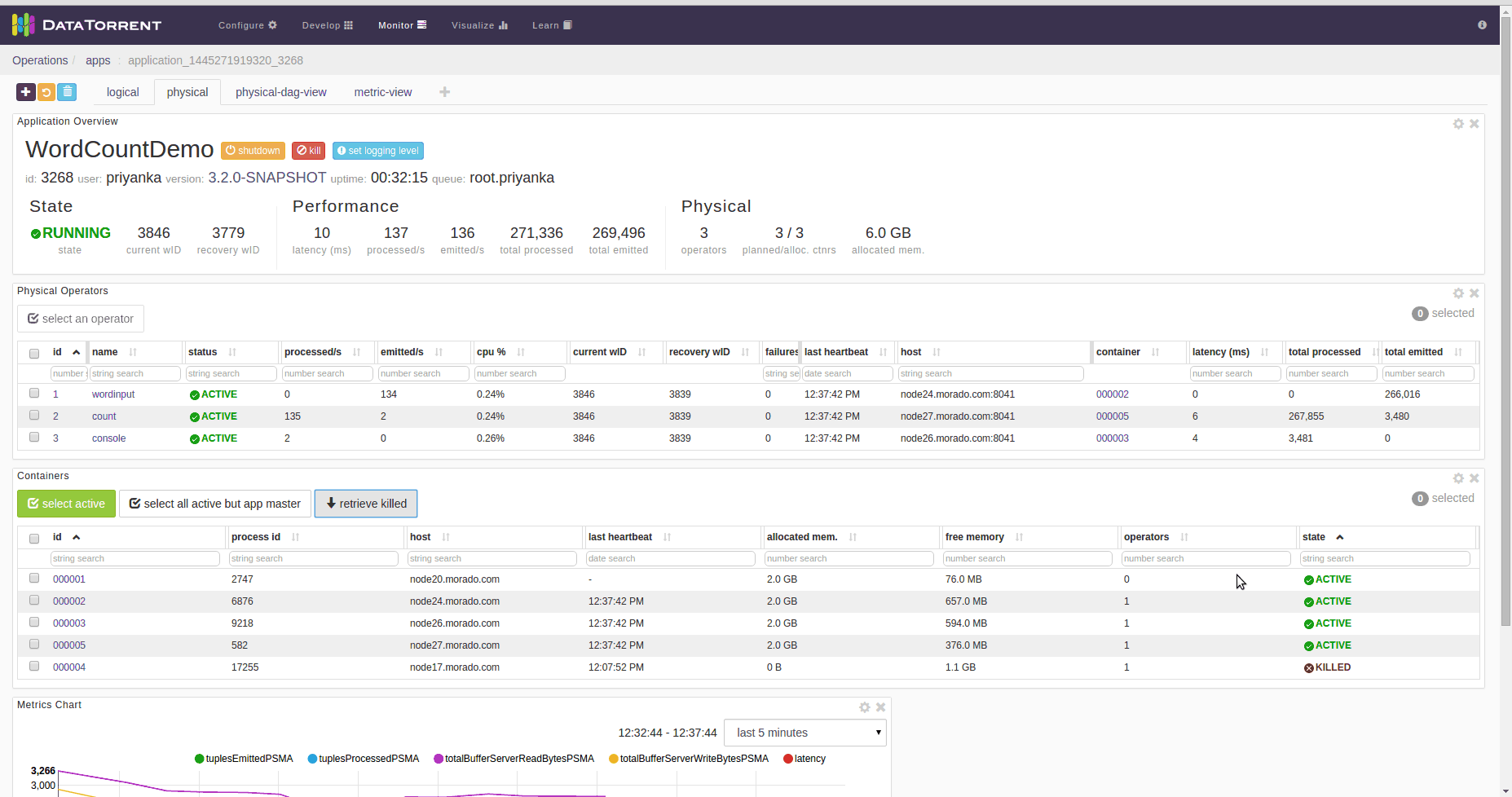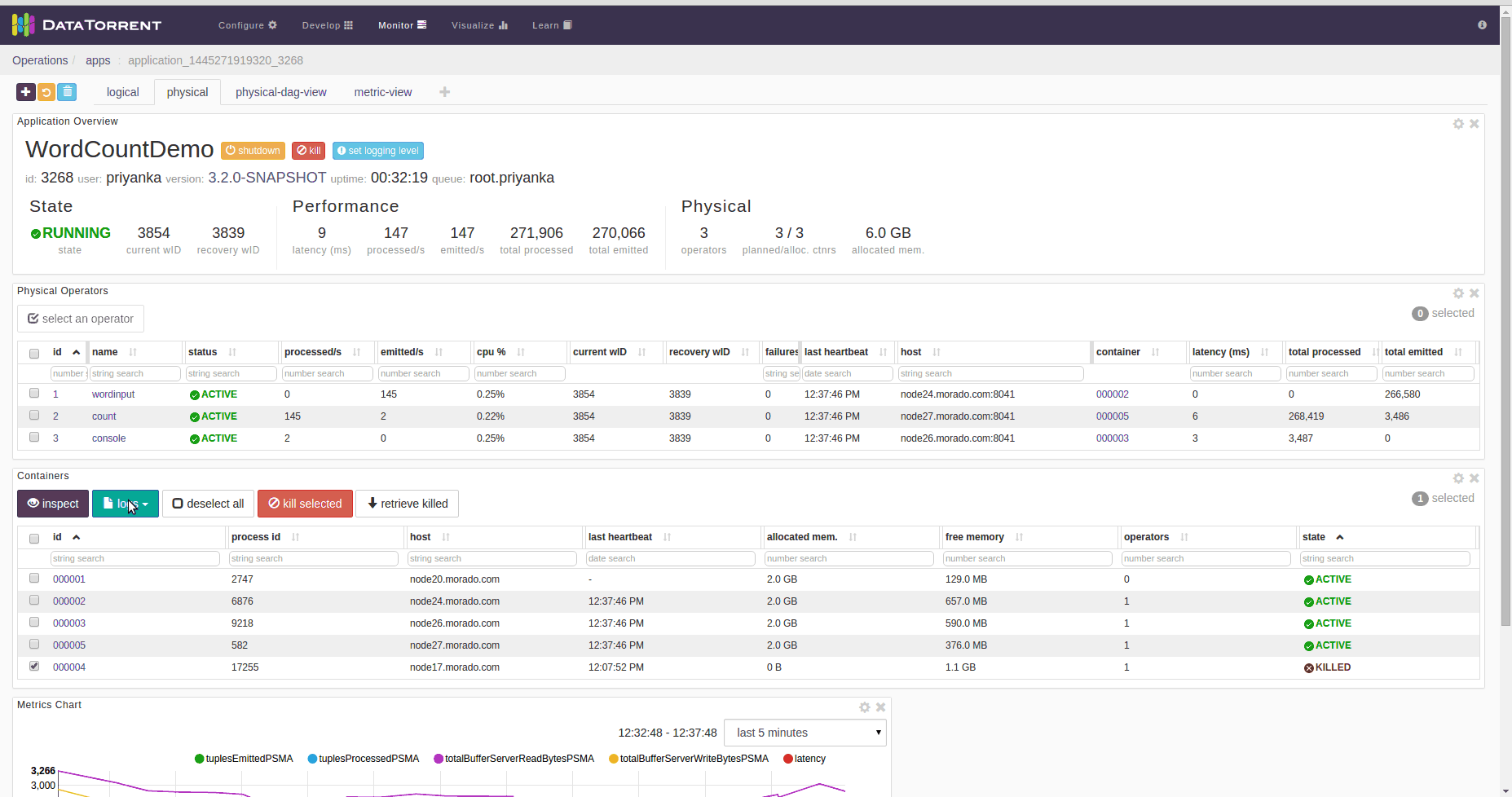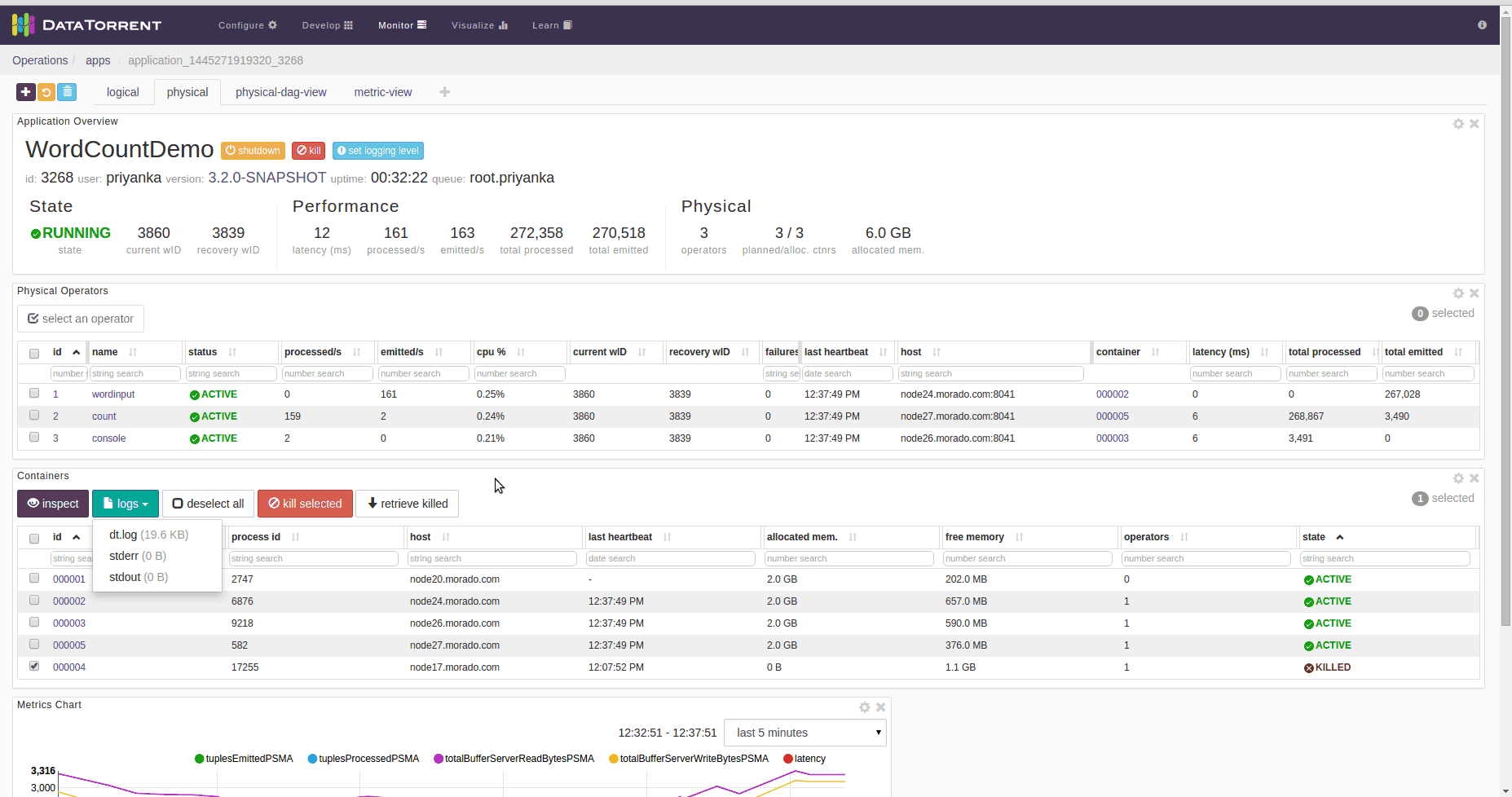
How to check killed operator’s state
On dt console, click on “retrieve killed” button of container List. Containers List widget’s default location is on the “physical” dashboard. Then select the appropriate container of killed operator and check the state.
How to search for particular any application or container?
In applications or containers table there is search text box. You can type in application name or container number to locate particular application or container.
How do I search within logs?
Once you navigate to the logs page,
- Download log file to search using your preferred editor
- use “grep” option and provide the search range “within specified range” or “over entire log”
Launching Applications
Application goes from accepted state to Finished(FAILED) state
Check if your application name conflicts with any of the already running
applications in your cluster. Apex does not allow two applications with
the same name to run simultaneously.
Your STRAM logs will have following error:
“Forced shutdown due to Application master failed due to application
\<appId> with duplicate application name \<appName> by the same user
\<user name> is already started.”
ConstraintViolationException during application launch
Check if all @NotNull properties of application are set. Apex operator properties are meant to configure parameter to operators. Some of the properties are must have, marked as @NotNull, to use an operator. If you don’t set any of such @NotNull properties application launch will fail and stram will throw ConstraintViolationException.
Events
How to check container failures
In StramEvents list (default location of this widget is in the “logical” dashboard), look for event “StopContainer”. Click on “details” button in front of event to get details of container failure.
How to search within events
You can search events in specified time range. Select “range” mode in StramEvents widget. Then select from and to timestamp and hit the search button.
tail vs range mode
tail mode allows you to see events as they come in while range mode allows you to search for events by time range.
What is “following” button in events pane
When we enable “following” button the stram events list will automatically scroll to bottom when new events come in.
How do I get a heap dump when a container gets an OutOfMemoryError ?
The JVM has a special option for triggering a heap dump when an Out Of Memory error
occurs, as well an associated option for specifying the name of the file to contain
the dump namely -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError and -XX:HeapDumpPath=/tmp/op.heapdump.
To add them to a specific operator, use this stanza in your configuration file
with <OPERATOR_NAME> replaced by the actual name of an operator:
<property>
<name>dt.operator.<OPERATOR_NAME>.attr.JVM_OPTIONS</name>
<value>-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=/tmp/op.heapdump</value>
</property>
To add them to all your containers, add this stanza to your configuration file:
<property>
<name>dt.attr.CONTAINER_JVM_OPTIONS</name>
<value>-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=/tmp/op.heapdump</value>
</property>
With these options, when an OutOfMemoryError occurs, the JVM writes the heap dump to the
file /tmp/op.heapdump; you'll then need to retrieve the file from the node on which the
operator was running.
You can use the tool jmap (bundled with the JDK) to get a heap dump from a running
container. Depending on the environment, you might need to run it as root and/or use
the -F option; here is a sample invocation on the sandbox:
dtadmin@dtbox:~$ sudo jmap -dump:format=b,file=dump.bin -F 15557
Attaching to process ID 15557, please wait...
Debugger attached successfully.
Server compiler detected.
JVM version is 24.79-b02
Dumping heap to dump.bin ...
Heap dump file created
The heap dump shows the content of the entire heap in binary form and, as such, is not human readable and needs special tools such as jhat or MAT to analyze it.
The former (jhat) is bundled as part of the JDK distribution, so it is very convenient
to use. When run on a file containing a heap dump, it parses the file and makes the data
viewable via a browser on port 7000 of the local host. Here is a typical run:
tmp: jhat op.heapdump
Reading from op.heapdump...
Dump file created Fri Feb 26 14:06:48 PST 2016
Snapshot read, resolving...
Resolving 70966 objects...
Chasing references, expect 14 dots..............
Eliminating duplicate references..............
Snapshot resolved.
Started HTTP server on port 7000
Server is ready.
It is important to remember that a heap dump is different from a thread dump. The latter shows the stack trace of every thread running in the container and is useful when threads are deadlocked. Additional information on tools related to both types of dumps is available here.
Coming Soon
- Connection Refused Exception
- ClassNotFound Exception
- Launching apa vs jar
- DAG validation failed
- Multiple gateways running simultaneously, app not launched.
- HDFS in safe mode
- Application stays in accepted state
- Some containers do not get resources (specially in case of repartition)
- Insufficient memory set to operator causes operator kill continuously.
-
Why is the number of events same/different at input and output port of each operator?
-
Shutdown vs kill option
- Why shutdown doesn’t work? (if some containers are not running)
- Can I kill multiple applications at same time?
- Killing containers vs killing application
- STRAM failures (during define partitions)
- Thread local + partition parallel configuration
- What to do when downstream operators are slow than the input operators.
- I am seeing high latency, what to do?
- appConf in ADT (inside apa file) vs conf option in Apex CLI
- Application keeps restarting (has happened once due to license agent during upgrade)
- Operator getting killed after every 60 secs (Timeout issue)
- How to change commit frequency
- Difference between exactly once, at least once and at most once
- Thread local vs container local vs node local
- Cluster nodes not able to access edge node where Gateway is running
-
Developers not sure when to process incoming tuples in end window or when to do it in process function of operator
-
How partitioning works
- How the data is partitioned between different partitions.
- How to use stream-codec
- Data on which ports is partitioned? By default default partitioner partitions data on first port.
- How to enable stream-codec on multiple ports. (Join operator?? where both input-ports needs to receive same set of keys).
-
pom dependency management, exclusions etc. eg: Malhar library and contrib, Hive (includes Hadoop dependencies, we need to explicitly exclude), Jersey(we work only with 1.9 version) etc
-
All non-transient members of the operator object need to be serializable. All members that are not serializable cannot be saved during checkpoint and must be declared transient (e.g. connection objects). This is such a common problem that we need to dedicate a section to it.
-
Exactly once processing mode. Commit operation is supposed to be done at endWindow. This is only best-effort exactly once and not 100% guaranteed exactly once because operators may go down after endWindow and before checkpointing finishes.
-
How to check checkpoint size. (large checkpoint size cause instability in the DAG).
- How to add custom metrics and metric aggregator.
- Example of how to implement dynamic partitioning.